Electroconductive hydrogels for wearable electronics. Credit: The University of Hong Kong
Synthetic hydrogels show great promise in tissue repair, drug delivery, medical implants and many other applications. Hydrogels functionalized with electrically conductive components can be used in bioelectronic devices for cardiac or neural interfaces, for applications such as neural prosthetics, cardiac patches and electronic skin.
A research team led by Dr. Lizhi Xu of the Department of Mechanical Engineering in the Faculty of Engineering at the University of Hong Kong (HKU) has recently developed a new type of electroconductive hydrogel with outstanding mechanical strength and manufacturability, creating opportunities for the engineering of various bioelectronic devices.
The innovation has been published in Nature Communications in an article entitled “Hybrid assembly of polymeric nanofiber network for robust and electronically conductive hydrogels.”
Synthetic hydrogels are water-rich polymeric materials resembling biological soft tissues. They are soft, porous, and biocompatible, enabling a physical interface between natural biological tissues and advanced biomedical tools. In particular, electroconductive hydrogels have attracted wide research attention, as they can be used in bioelectronic devices for cardiac or neural interfaces.
“Existing hydrogels are mechanically weak and difficult to manufacture, which limits their practical utility. We used a unique microscale scaffold for the synthesis of conductive hydrogels. The architecture of the composites provided a combination of properties inaccessible by other hydrogels, which is crucial for realistic applications in bioelectronic devices,” said Dr. Xu.
For the new hydrogels developed by Dr. Xu’s team, a 3D nanofiber network was utilized as a template to guide the assembly of conducting polymers (such as polypyrrole). The high connectivity of the nanofibers provided both structural robustness and an effective pathway for electron conduction.
“For potential biomedical applications, the device needs to withstand repeated mechanical loading associated with body motion. In this regard, mechanical robustness of the materials would be very important,” Dr. Xu explained.
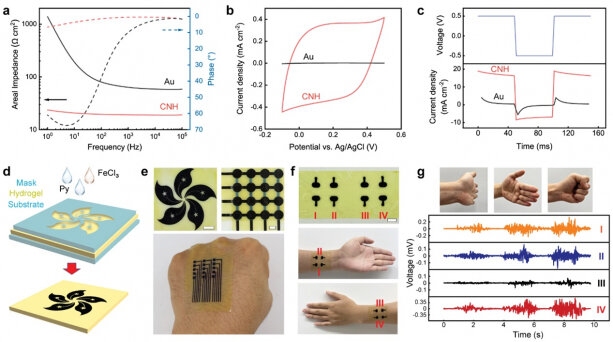
The resulting material developed by the team contains 80% water by weight, while at the same time showing a high electrical conductivity of ~80 S/cm and a mechanical strength of ~9.4 MPa.
“These conductive hydrogels are easy to fabricate. One can pattern them into arrays of electrodes, interconnects, and biosensors, enabling functional systems such as wearable health monitors or cardiac tissue engineering platforms,” Dr. Xu said.
“It opens opportunities for many advanced medical tools down the road, such as neural prosthetics, cardiac patches, electronic skin, and so on,” He added.
Dr. Xu and his research team earlier created another novel type of hydrogel that mimics tendons, exhibiting remarkable mechanical properties that closely resemble those of natural tendons, along with multiple functionalities that are well-suited for biomedical applications.
More information: Huimin He et al, Hybrid assembly of polymeric nanofiber network for robust and electronically conductive hydrogels, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36438-8
Provided by The University of Hong Kong
Citation: Engineers develop electroconductive hydrogel for biomedical applications (2023, May 3) retrieved 30 May 2023 from https://phys.org/news/2023-05-electroconductive-hydrogel-biomedical-applications.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.