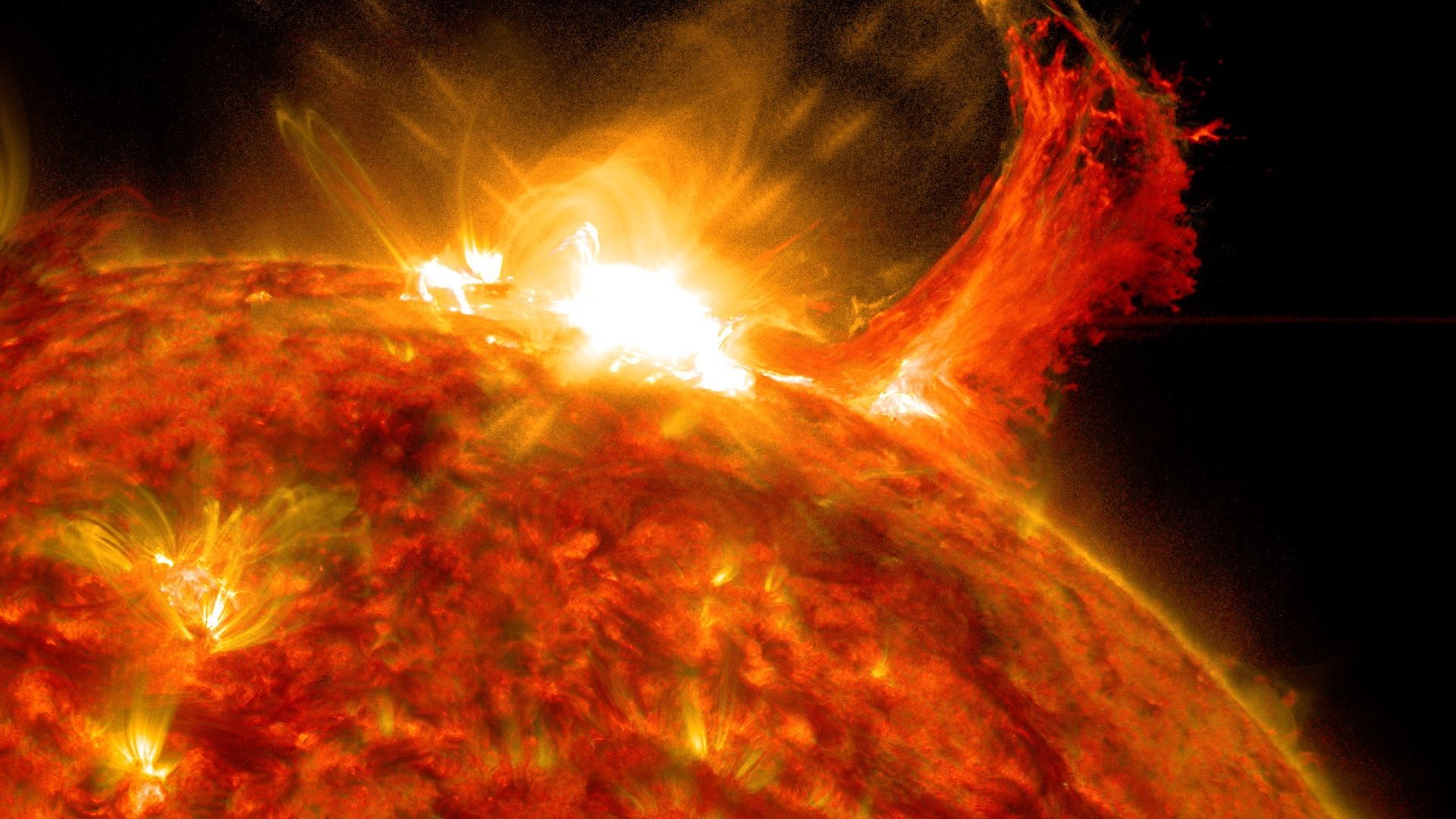
A hot mystery on the sun may be close to being solved.
For decades, scientists have been trying to understand why the sun‘s outer atmosphere is so much hotter than its surface, despite being farther from the core. Whereas the surface, or photosphere, is millions of degrees Fahrenheit, the outer atmosphere is only about 10,000 F (5,500 C).
New data from the National Science Foundation’s Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (DKIST) in Hawaii — the largest ground-based solar telescope ever built — is helping scientists learn how the sun’s energy is transported through its atmosphere.
A solar mystery
Researchers previously noted the extreme temperature of the sun’s corona, as well as the supercharged flow of heated gas, called the solar wind, which streams from the sun at more than 1 million mph (1.6 million km/h), said Richard Morton, a solar physicist and professor at Northumbria University in the U.K. who led the research, told Live Science in an email.
Both processes need energy, and scientists assumed rolling convection at the sun’s surface generated the requisite fuel. But complications arose during the first studies of this decades ago.
“It is unclear how this [energy] gets transferred into the atmosphere and solar wind, and how the energy is converted to heat and momentum,” Morton said.
In 1942, Swedish plasma physicist (and eventual Nobel Prize winner) Hannes Alfvén suggested magnetic waves may be responsible. But these waves, now known as Alfvén waves, had never been spotted in the corona until now.
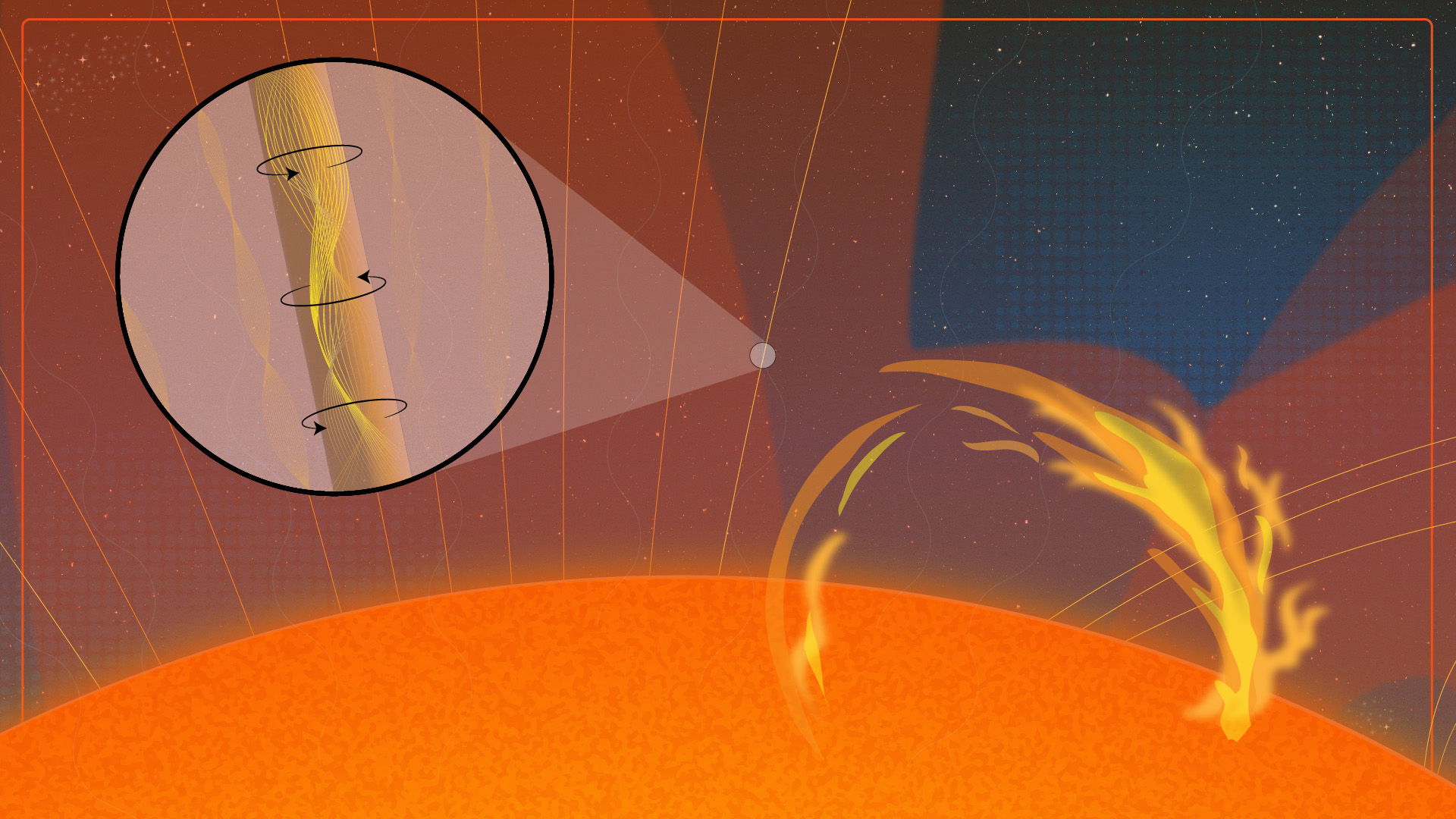
“This was because the sensitivity of previous instrumentation has not been good enough to resolve the motions of the Alfvén waves,” Morton said. “Despite this, many numerical experiments and space weather forecasting tools assume that Alfvén waves exist in the corona. However, the properties of the waves they use within the models have been educated guesses.”
‘Unprecedented’ observations
DKIST has a 4-meter (13 feet) mirror and an “unprecedented” resolution of the sun, Morton said, with much “cleaner measurements” (less noise) than any prior solar observatory. In the new research, scientists used the telescope’s Cryogenic Near Infrared Spectropolarimeter (Cryo-NIRSP) to search for the coronal Alfvén waves.
Cryo-NIRSP can chart movements of the corona through images, Morton said, as well as examine changes in the sun’s plasma (superheated gas) through a phenomenon known as Doppler shift — the perceived difference in the frequency of a wave as the observer and the source of the wave move toward or away from each other. (A common, real-life example is the change in the sound of an ambulance siren as it passes by a pedestrian on the street.)
“Cryo-NIRSP provided the data to enable us to observe the tell-tale signature of the Alfvén waves, which in a plasma like the corona, is a back-and-forth twisting of the magnetic field,” Morton said. “This appears as an alternating pattern of red and blue Doppler shifts on opposite sides of the magnetic fields. We found these waves were continually present during the time of observation, and given there was nothing particularly special about the region we observed, this implies they are always likely common across the rest of the atmosphere.”
“Perhaps most importantly,” he continued, “our analysis indicates that waves likely carry a significant amount of energy.”
That is a significant finding, he noted, because astronomers have been debating between solar waves and magnetic reconnection — when magnetic fields on the sun twist together and snap, releasing energy — as the mechanism behind the intense heating in the corona.
While various spacecraft have found evidence that magnetic reconnection is a driver of coronal heating, the new findings from DKIST show that the full picture is more complicated. Solar observatories such as NASA‘s Parker Solar Probe and the European Space Agency’s Solar Orbiter, alongside the fresh data from DKIST, show “both waves and reconnection are occurring frequently throughout the Sun’s atmosphere,” Morton said.
“Our research confirms that the Alfvén waves are present and carry a significant amount of energy, potentially making up at least half the required energy for heating the corona,” he added. “However, the exact energy associated with the waves is still challenging to estimate.”
The ratio of magnetic reconnection to Alfvén waves affects not only solar heating but also the light (or more properly, the radiative output) from the sun, as well as the light from stars beyond our solar system. Scientists hope to use the research to understand how planetary systems evolved over the longer term and to make better short-term predictions about solar wind production. “It is hoped that further studies like the one we have published will shed some light on the properties of Alfvén waves to better inform the models and improve predictions,” he said.

