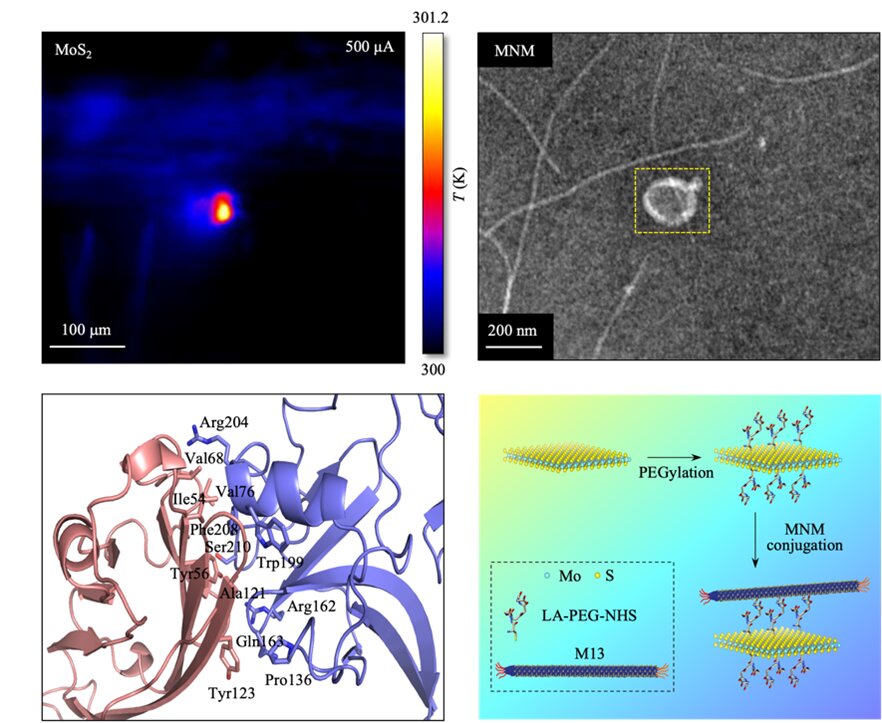
Top left, Thermograph of the sample upon application of electrical signal; Top right, Transmission electron microscopy image of MNM; Bottom left, Binding interface of the virus-cancer cell protein structure; Bottom right, Schematic diagram of the composition and process used to construct the MNM. Credit: Pharmaceutics (2022). DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010106
Electro-thermal therapy, which involves applying electrical signals to nanomaterials, provides high cancer cell targeting accuracy and is highly bio-compatible. In this research, scientists from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) have designed a novel thermal-based therapy nano-system that destroys more than 20% of pancreatic cancer cells using microsecond electrical pulses and with excellent bio-compatibility.
Electro-thermal therapy works by injecting two dimensional (2D) materials in cancer cells and applying electrical currents to the cells. This causes the materials to heat up and kill neighboring cancer cells. Traditional electro-thermal therapy with 2D materials however, can fail as a result of weak cancer cell ablation. This is due to the limited amount of materials assembled on the cancer cells and the weak Joule heating generated in the material.
To alleviate these issues, the researchers deposited the M13 virus on molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) layered materials to create a hybrid nanomaterial MoS2 Nanostructure with M13 virus (the authors call it MNM). Moreover, they altered the nanomaterial surfaces with polyethylene glycol (PEG) to improve bio-compatibility.
The introduction of the M13 virus improves the electro-thermal therapy performance. Compared to conventional 2D materials, a larger amount of MNM assembles on the cancer cells due to the higher specificity of the binding of the M13 virus to cancer cells. Due to the high electrical conductivity of the MoS2 material, a strong Joule heating is also generated.
As a result, a larger amount of heat is produced in the nanomaterials, and can be used to kill a larger population of the cancer cells. For example, the MNM nanosystem can decrease the percentage of cancer cells by 23%, which is approximately 2 times higher than what current thermal-based therapy nano-systems can do.
“For many years, cancer eradication has been the dream of cancer patients and researchers. Eliminating recurrence and metastasis of the cancer in the body is of vital importance,” says principal investigator, Assistant Professor Desmond Loke from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD).
“However, a single conventional therapy is unable to eradicate cancer cells completely, due to the diversity, heterogeneity, and complexity of the cancer cells. This is why we aimed to design a simple nanosystem or nanomaterial to synergistically eradicate and treat cancer cells.”
The paper is published in the journal Pharmaceutics.
More information: Maria P. Meivita et al, An Efficient, Short Stimulus PANC-1 Cancer Cell Ablation and Electrothermal Therapy Driven by Hydrophobic Interactions, Pharmaceutics (2022). DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010106
Provided by Singapore University of Technology and Design
Citation: Researchers develop a novel 2D material that uses a virus to kill cancer cells (2023, February 16) retrieved 5 March 2023 from https://phys.org/news/2023-02-2d-material-virus-cancer-cells.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.