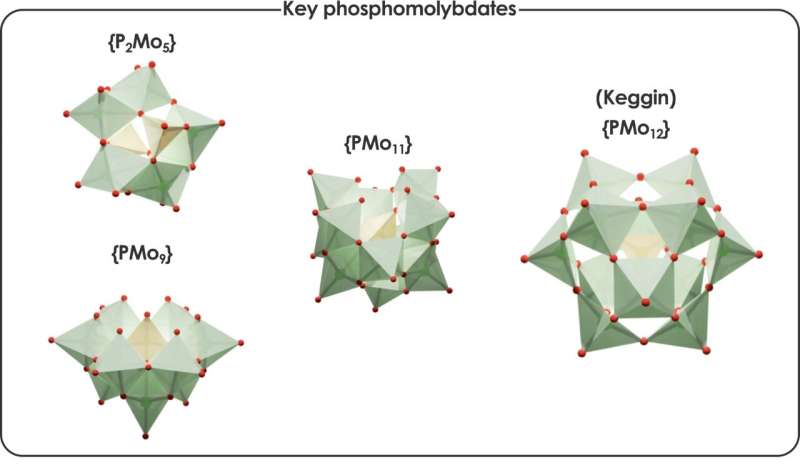
Researchers from the group of Prof. Carles Bo at the Institute of Chemical Research of Catalonia (ICIQ-CERCA) have described a computational methodology that simulates complex processes involving different chemical species and diverse conditions. These processes lead to the formation of nanostructures called polyoxometalates (POMs), with important applications in catalysis, energy storage, biology and medicine.
The work appears in Chemical Science.
“Our group has recently developed unique methods to study the chemistry of polyoxometalates in solution, their speciation and formation mechanisms. This research has the potential to discover the experimental conditions needed to make new materials,” explains Prof. Bo.
Versatile POMs
POMs are a distinguished family of nanostructures composed of transition metal atoms linked by oxygens, forming a wide range of well-defined structures of different sizes and shapes. These nanostructures are formed via self-assembly processes of simple metal oxides, depending on different factors such as pH, temperature, pressure, total metal concentration, ionic force, and the presence of reducing agents and counter-ions. The sum of all these conditions complicates the control of their synthesis.
Researchers can now predict the effect of these factors and the suitable conditions to produce one specific species of POM, employing statistical methods that facilitate the efficient and scalable processing of numerous speciation models and their corresponding systems of non-linear equations. This is important, as the first key application of these nanostructures is related to catalysis, where POMs are known to accelerate several important reactions. For example, using these simulations, it is possible to describe the suitable conditions that lead to the production of a species of POM responsible for catalyzing CO2 fixation.
POMSimulator
The group of Prof. Bo has presented an open–source software package named POMSimulator that helps clarify the formation mechanisms of POMs. By releasing a public version of the code, the researchers aim to provide a tool for complementing the discovery of novel POMs. Moreover, having an accessible version of the code means that other researchers can modify the source code based on their needs.

The methodology now presented is a more robust version of this POMSimulator that provides new and valuable insights into the distribution of species under different chemical conditions, thereby enriching the knowledge of complex systems speciation.
“In the times of Big Data, machine learning and artificial intelligence, it is crucial to use every bit of information in our hands. Our work has taken POMSimulator to the next level of data usage,” said Jordi Buils, first author of this work and Ph.D. student in Prof. Bo’s group.
More information:
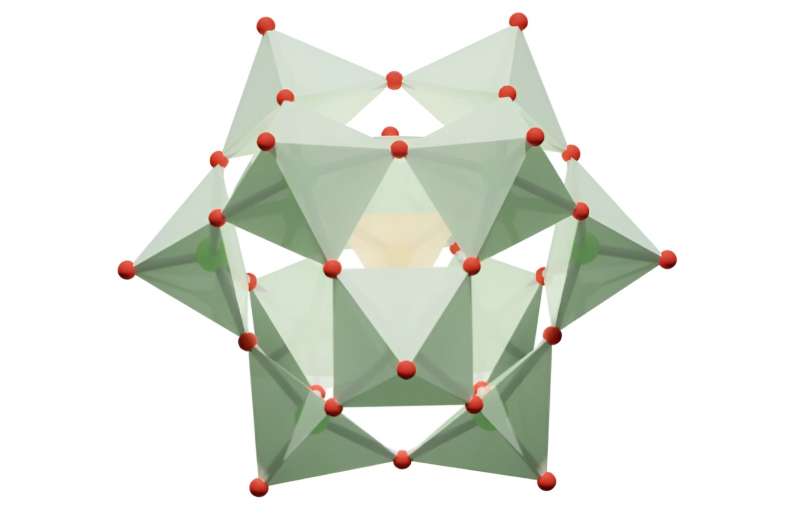
Jordi Buils Casasnovas et al, Computational Insights into Aqueous Speciation of Metal-Oxide NanoClusters: An In-Depth Study of the Keggin Phosphomolybdate, Chemical Science (2024). DOI: 10.1039/D4SC03282A
Provided by
Institute of Chemical Research of Catalonia
Citation:
New computational methodology to predict the complex formation of interesting nanostructures (2024, August 20)
retrieved 20 August 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-08-methodology-complex-formation-nanostructures.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.

