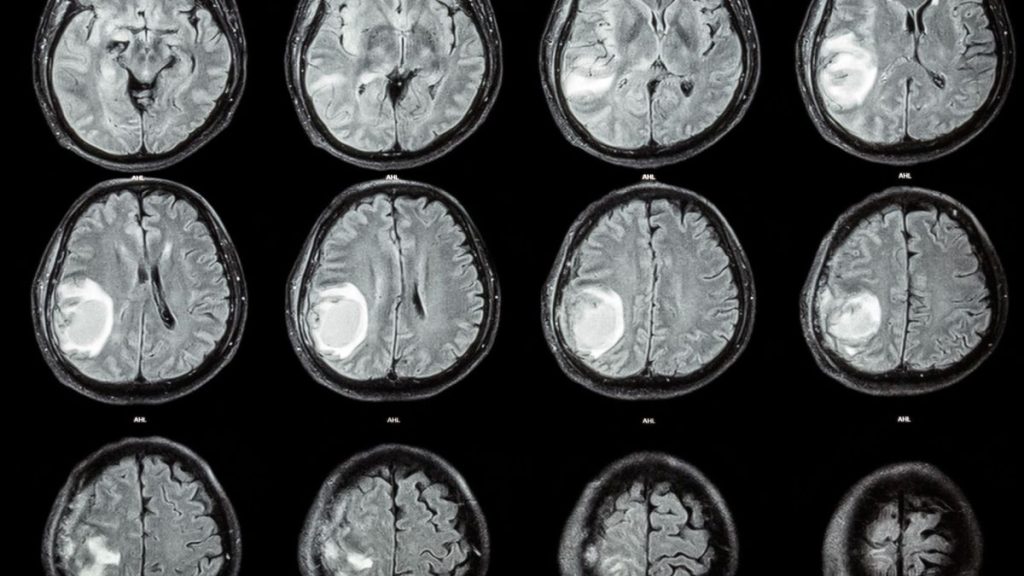
In an extremely rare case, doctors surgically removed a fetus from the brain of a 1-year-old child. Doctors found the fetus after the child showed delayed motor skill development, an enlarged head circumference and a buildup of fluid in the brain.
The report, published Dec. 12, 2022, in the journal Neurology (opens in new tab), noted that the mass in the young child’s head was a “malformed monochorionic diamniotic twin,” meaning in the womb, the fetuses had once shared the same placenta but had separate amniotic sacs, the thin-walled, liquid-filled sacs that surround fetuses as they develop. These types of twins come from the same fertilized egg, meaning they’re identical.
The anomaly in which one fetus becomes enveloped by another is known as “fetus in fetu,” or sometimes “parasitic twin.” The absorbed twin typically stops developing while the other continues to grow, the Miami Herald reported (opens in new tab).
The phenomenon occurs in an estimated 1 in 500,000 live births (opens in new tab); usually, the malformed fetus appears as a mass in the other fetus’s abdomen, wedged behind the tissues that line the abdominal wall. However, in this case, the mass appeared in the “host” fetus’s head, and likely arose very, very early in development, at the stage when the fertilized egg forms a cluster of cells called a blastocyst.
Related: Did you share the womb with a ‘vanishing twin’? The answer may be written in your DNA.
“The intracranial fetus-in-fetu is proposed to arise from unseparated blastocysts,” meaning the cell clusters that were destined to grow into two separate fetuses stayed stuck together, the case report authors wrote. “The conjoined parts develop into the forebrain of host fetus and envelop the other embryo during neural plate folding.” (The neural plate is a structure that forms in early development and gives rise to the nervous system.)
“Intracranial fetus in fetu is extremely rare with <20 reports published worldwide," a 2020 case report in the journal World Neurosurgery (opens in new tab) noted.
Brain scans of the 1-year-old child’s head revealed that the fetus contained a vertebral column and two leg bones (the femur and tibia), and that the malformed fetus had spina bifida, a condition in which part of the spinal cord is exposed, rather than covered by tissues of the back, due to a problem during development. Once removed, the fetal mass was also determined to have “upper limb and finger-like buds.”
The brief case report does not include details of the 1-year-old’s condition following surgery.