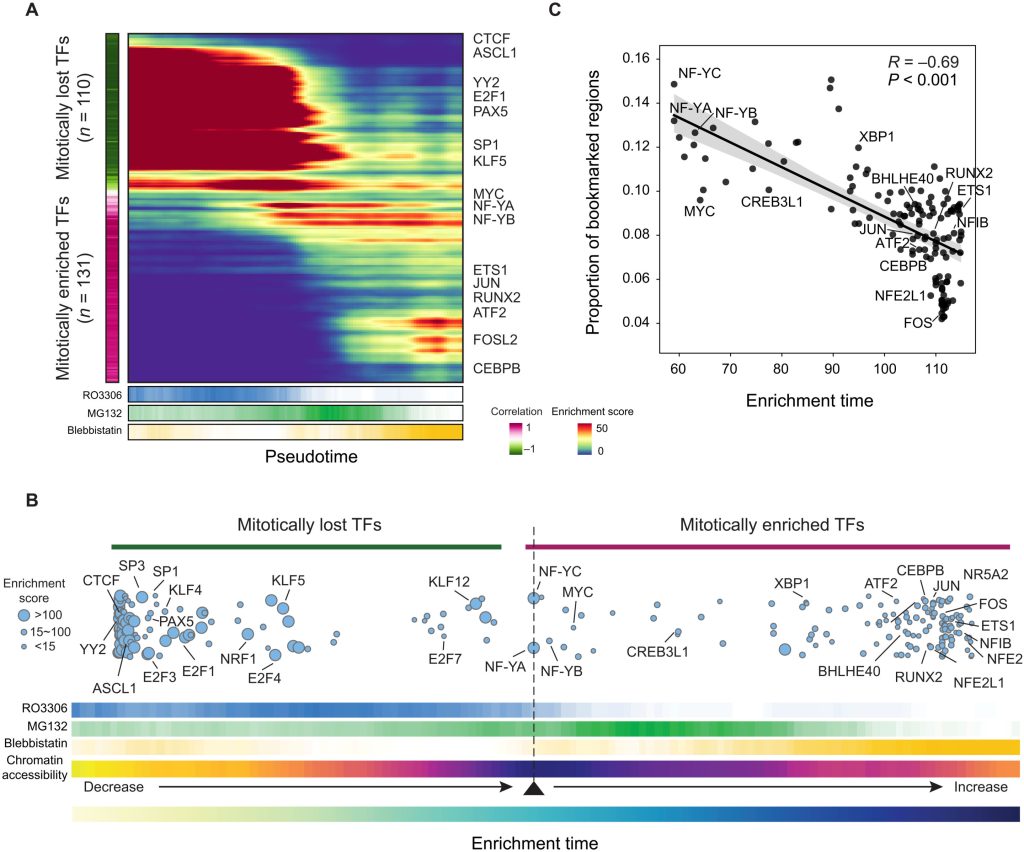
Dynamics of transcription factor enrichment during mitosis.(A) Heatmap showing the enrichment score of the 241 TFs along the pseudotime trajectory. The color bar to the left of the heatmap indicated the Pearson correlation coefficient (ρ) between TF’s enrichment score and pseudotime. (B) Bubble plots showing the dynamics of TF occupancy to chromatin along the pseudotime trajectory. The position of each bubble along the x axis indicated the pseudotime at which the TF reached its maximum enrichment score, which was defined as the TF’s enrichment time. The size of the bubble represented the average enrichment score of that TF in the pseudotime trajectory. The color bar in the bottom indicated the proportion of each drug-treated group in the window, chromatin accessibility, and enrichment time along the trajectory. (C) Scatter plot showing the Pearson correlation between TF enrichment time and the proportion of bookmarked regions in TF-targeted regions. Each dot represented a mitotically enriched TF, and the TF-targeted regions were defined as the open regions containing the TF motif. Credit: Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.add2175
Recently, a team led by Prof. Qu Kun from the University of Science and Technology (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) in collaboration with a team led by Prof. Wang Zhikai from the Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale (HFNL) revealed a dynamic and regulatory map of chromatin accessibility that reveals important bookmarking factors. The result was published in Science Advances.
Mitosis is accompanied by changes in histone, the loss of chromatin accessibility and the silencing of gene transcription. However, there are emerging observations indicating that some chromatin features are partially or completely preserved during mitosis, conveying gene regulatory architectures like “bookmarks,” which is known as “mitotic bookmarking.”
The structural and functional states of active genes could be bookmarked to ensure their proper reactivation after mitosis, which is essential for the transmission of transcriptional memory from mother cells to daughter progenies.
In the study, researchers used the plate-based single-cell transposase accessible chromatin sequencing (scATAC-seq) technique to analyze 6538 mitotic cells and characterize the dynamics of chromatin accessibility during mitosis. Using pseudotime inference anaylsis, they got a two-dimensional map of the chromatin accessibility of the cells and found that chromatin accessibility continued to decrease after mitotic entry and then began to increase at the metaphase-anaphase transition.
Based on the map, they found a subset of chromatin regions that remained open throughout mitosis and defined it as “bookmarked regions.” These regions were enriched in promoters of genes that were rapidly reactivated after mitosis.
As open chromatin is often occupied by transcription factors (TFs), the researchers investigated which TFs exert potential regulatory functions after metaphase. Using TF binding motif enrichment analysis, they found that the nuclear transcription factor Y subunit α(NF-YA) motif CCAAT is the most enriched motif in these regions.
They further demonstrated that NF-YA functioned as a bookmarking TF by preferentially occupying the bookmarked regions, and NF-YA knockdown (KD) impaired chromatin accessibility expansion and transcriptional reactivation upon mitotic exit. They confirmed the bookmarking role of NF-YA by performing a depleting experiment, whose result is consistent with the conclusion.
More information: Qiaoni Yu et al, Dynamics and regulation of mitotic chromatin accessibility bookmarking at single-cell resolution, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.add2175
Provided by University of Science and Technology of China
Citation: Examining the dynamic and regulatory blueprint of mitotic bookmarking (2023, March 15) retrieved 9 April 2023 from https://phys.org/news/2023-03-dynamic-regulatory-blueprint-mitotic-bookmarking.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.