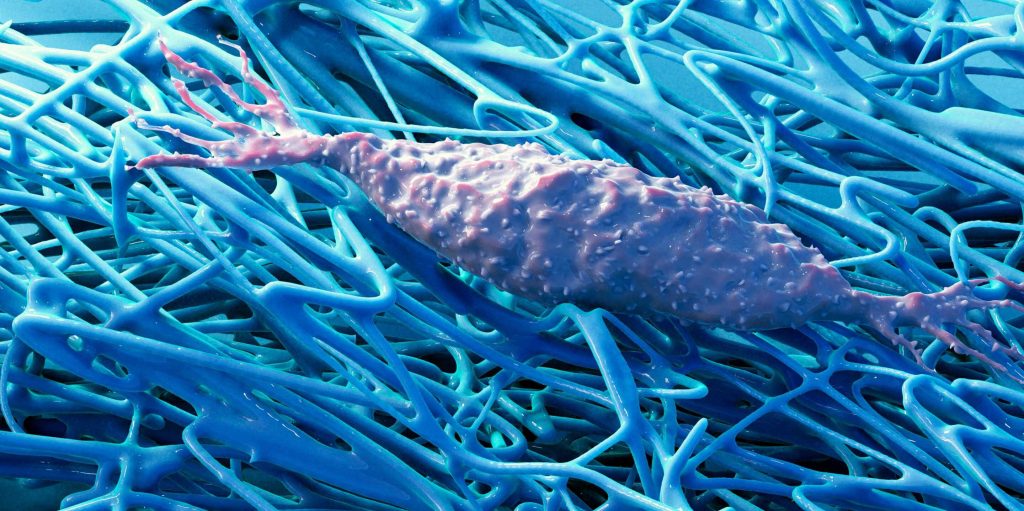
Fibroblasts (centre) surround themselves with a fibrous matrix. Via special membrane proteins, they are able to sense mechanical stimuli from this extracellular matrix. Credit: Science Photo Library
How does an embryo develop? How do children grow, wounds heal or cancer spread? All of this has to do with the growth of body tissue. One of the major research interests of ETH Professor Viola Vogel and her senior assistant Mario C. Benn is to understand this growth in detail. In their quest, they have departed from well-trodden research paths.
For a long time, biology was about studying cells and the biochemistry of the metabolic processes within them, often regardless of their natural environment. Vogel and Benn, by contrast, are focusing on the extracellular matrix (ECM), a fibrous structure that surrounds body cells. This matrix is produced by the cells themselves and is a major component of all tissue.
There are many different interactions between body cells and this fibrous matrix. In recent years, research has increasingly shown that not all of these interactions are exclusively biochemical. In fact, some are mechanical or physical. For example, cells are capable of sensing mechanical stimuli from this extracellular matrix.
Together with their team of researchers, Vogel and Benn have now been able to replicate tissue growth in vitro and study this process in detail. “Our results underline the importance of the interactions between cells and the extracellular matrix,” Benn says. In time, he hopes to make medical use of these findings—to prevent wound-healing disorders, for example, or in the therapy of cancer and connective-tissue diseases.
Cell transformation
Their study, now published in Science Advances, focused on two cell types: fibroblasts and myofibroblasts. Each of them is important for human tissue functionality, and each one can change into the other. Fibroblasts are found in the connective tissue of our organs, where they ensure that the extracellular matrix is continuously renewed and remains healthy. If an injury occurs or tissue growth is required, the fibroblasts transform into myofibroblasts, which play a key role in healing wounds and the growth of new tissue. Myofibroblasts not only produce large amounts of ECM but are also strong enough, for example, to pull together tissue in wounds.
“When it comes to wound healing, myofibroblasts are our friends,” Benn says. Once their work is done, however, it is important that these myofibroblasts change back into the less active fibroblasts. If not, this can lead to fibrosis—the excessive formation of scar tissue. Myofibroblasts are also found in cancer tissue. For many cancers, high levels of these cells is associated with a poor prognosis.
Three-dimensional matrix
Some things are known about the biochemical processes that take place when myofibroblasts revert to fibroblasts. Yet little research has been done to explain how the ECM influences this cellular transformation. “With conventional cell-culture methods, the cells grow flat across the culture dish. This leads to the formation of an unnaturally planar ECM,” Vogel explains. “And anyway, research up to now has generally ignored the ECM. But studying cells without the extracellular matrix is a bit like studying the behavior of spiders without their web.”
Cells progressively fill the cleft with new tissue, starting at the apex on the left. Myofibroblasts at the growth front are highlighted in orange (microscope image). Credit: Benn MC et al, Science Advances, March 2023; image enhanced
The method used by Vogel and Benn is quite different. It was originally developed at the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces in Potsdam and has now been refined by the ETH scientists. They use a silicone scaffold, coated with specific proteins, that has microscopic triangular-shaped clefts and sits in a tissue culture medium. Over a two-week period, new tissue forms in these clefts, together with a more natural ECM. Growth begins at the apex, progressively filling the cleft as the tissue grows.
The researchers observed how myofibroblasts are always located precisely at the growth front—i.e., in the area of the tissue that is being newly formed. They were also able to show how myofibroblasts in this area form new ECM—initially in a provisional and then in a more stable form—before converting back into fibroblasts. “The processes are similar to those that take place in human subcutaneous tissue during the late phase of wound healing,” Benn says.
The researchers were also able to show that rapidly changing ECM is one of the triggers for the reversion of myofibroblasts to fibroblasts. Moreover, this reversion is promoted when a certain type of ECM fiber—fibronectin—changes from a stretched to a relaxed state. It seems likely that similar interactive processes occur during wound healing.
The researchers then purposely interfered with the cell transition using various agents that change the composition or structure of the extracellular matrix. In this way, they were able to replicate what occurs with pathologies such as fibrosis or cancer—namely, that instead of reverting to fibroblasts as in healthy tissue, the myofibroblasts are stabilized by the extracellular matrix.
Future mechano-medicine
The researchers hope that such miniature tissue cultures will help them decipher further details of the interaction between human cells and their extracellular matrix. This will not only avoid animal testing, which otherwise is often necessary in biomedical research; it is also a method that in future could be used to test candidate substances during drug development. “These applications and research questions are low-hanging fruit,” Benn explains. “If we can understand how myofibroblasts and fibroblasts change into one another, and control that process, then we can also make major progress with conditions such as wound-healing disorders, fibrosis and cancer.”
Benn and Vogel also refer to a future field called mechano-medicine. This term describes the medical application of findings from the field of mechanobiology: the study of how cells can sense and process mechanical signals. In other words, mechano-medicine aims to apply the insights gained from mechanobiology to medical practice.
In time, the researchers hope to use mechano-medicine in the development of new diagnostic methods for the early detection of fibrotic tissue. “With many conditions, including pulmonary fibrosis, successful treatment depends on early detection,” Benn says.
Current screening methods are unable to detect myofibroblasts in lung tissue with any great accuracy. Benn now hopes that further study of the extracellular matrix will reveal biomarkers that enable earlier and easier detection of fibrosis and similar connective-tissue diseases.
More information: Mario C. Benn et al, How the mechanobiology orchestrates the iterative and reciprocal ECM-cell cross-talk that drives microtissue growth, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.add9275
Citation: How cells are influenced by their environment as tissues grow (2023, May 3) retrieved 23 May 2023 from https://phys.org/news/2023-05-cells-environment-tissues.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.